Practical Security Tips
Protecting your site from hackers is crucial to safeguard your data, user information, and your brand’s reputation. Hacker attacks are getting more sophisticated, so it’s important to take security measures to keep your site as safe as possible. Below, we explain several key practical tips to help you protect your site from attacks.
Use Strong Passwords
One of the most basic yet crucial steps to protect your site is using strong and unique passwords. Many hacking methods, like brute-force attacks, rely on guessing passwords. Recommended:
- 1. Password length: Passwords should be at least 12 characters long.
- 2. Variety: Use a mix of uppercase, lowercase, numbers, symbols, and special characters.
- 3. Unique passwords: Don’t reuse passwords across multiple sites.
To generate and securely store passwords, use password managers (e.g., LastPass, Bitwarden) that save your passwords and enable automatic form filling on sites.
Regularly Update Software and Plugins
Your site’s software, including CMS (like WordPress), themes, and plugins, often have security vulnerabilities that hackers exploit. Hackers frequently target sites running outdated software because unpatched weaknesses are easy to find.
- 1. Enable automatic updates: Turn on automatic updates for WordPress, plugins, and all other apps you use. If you use a custom CMS, regularly check and install the latest patches.
- 2. Perform regular checks: Follow new security patches and notifications from developers and develop a habit of updating your system regularly.
Use SSL Encryption (HTTPS)
SSL (Secure Socket Layer) encrypts data sent between your server and users, preventing unauthorized access. With an SSL certificate, your website URL will use "https" instead of "http", signaling users that your site is secure.
SSL protection matters because:
- 1. It encrypts data: Users entering personal or payment info can be sure their data is safe.
- 2. SEO benefits: Google favors sites with SSL certificates, which can boost your search rankings.
You can get SSL certificates from certified providers like Let's Encrypt (free SSL), and many hosting providers include them in their packages.
Use Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) is a security method that adds an extra layer of protection. Instead of relying solely on a password, users must complete a second verification step, like entering a unique code sent to their phone or email.
- 1. Stronger protection: Even if someone gets your password, without the second factor they can't access your account.
- 2. Easy to implement: Many popular platforms (like WordPress) offer plugins for two-factor authentication.
Regularly Back Up Your Website
Even if you take all security measures, there's always a risk of an attack. To be prepared for the worst-case scenario, make regular backups of your website. If an attack happens, your backup lets you quickly restore the site to its original state.
- 1. Automatic backups: Set up automatic backups daily, weekly, or monthly.
- 2. Backup storage: Store backups in secure locations like external servers or cloud services (Google Drive, Dropbox).
Limit Access and Permissions
One key tip is to limit who can access your site's admin functions. No one except you and trusted users should have access to sensitive features like site settings and databases.
- 1. Reduce user count: Keep the number of admin users to a minimum.
- 2. Access rights: Assign only necessary privileges. For example, regular users shouldn’t have access to site settings.
- 3. IP filtering: If possible, restrict access by IP address to allow only authorized users.
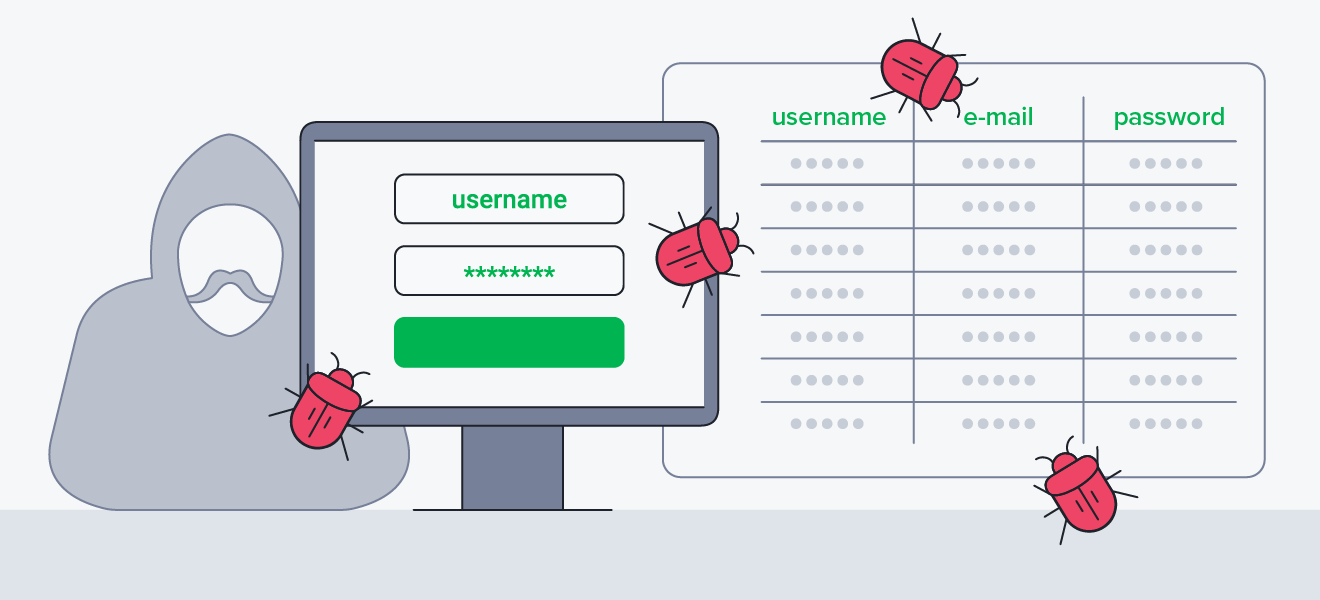
Install a Firewall
A Firewall monitors and controls traffic between your website and the internet. It can block unauthorized access attempts and prevent many common attacks.
- 1. Web Application Firewall (WAF): A specialized firewall that protects web applications. For example, it can block SQL injections and Cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks.
- 2. Cloudflare: A popular service offering WAF, DDoS protection, and much more.
Website Monitoring and Security Checks
Continuous website monitoring is essential for detecting attacks early. Track suspicious activities on your site, such as sudden traffic spikes or unusual server requests.
- 1. Monitoring tools: Tools like Sucuri or Wordfence can scan your site and identify potential security threats.
- 2. File checks: Regularly check your site files to detect unauthorized changes or infected files.
Secure Your Database
Your website's database is very sensitive and must be protected against intrusion attempts. Attacks like SQL injections can allow hackers to access sensitive data, such as user information or transaction details.
- 1. Database security: Use secure access credentials, such as strong passwords, and restrict access only to necessary IP addresses.
- 2. Security patches: Regularly update your database and enable backups.
Train Users and Administrators
Protecting your site isn't just about tech. It's crucial that both admins and users understand potential security threats. Training users on security best practices can make a big difference.
- 1. Phishing attacks: Educate users on how to recognize phishing attempts (e.g., fake emails and websites).
- 2. Access policies: Teach users and admins to use secure authentication methods and access controls.
Conclusion
Protecting your website from hackers is an ongoing process that requires constant attention and dedication. By applying these security tips, you can significantly reduce the risk of attacks and maintain the safety of your data and users. Although no protection is 100% foolproof, these measures will help you build a strong defense and lower the chances of a successful breach.